Building Your EMR System Integration Foundation
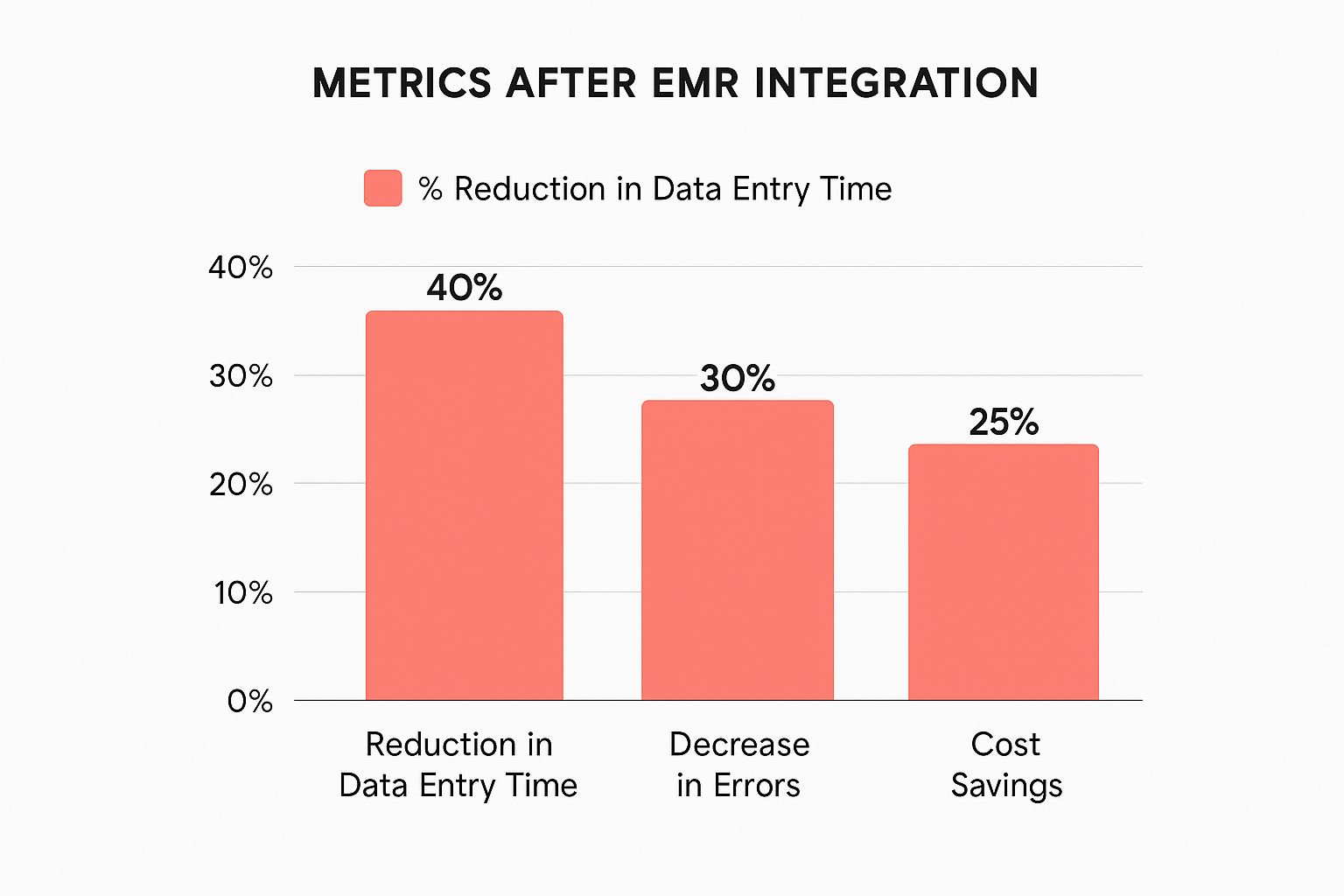
The infographic above illustrates how effective EMR system integration impacts three key areas: data entry time, error rates, and cost savings. Streamlined integration demonstrably leads to significant improvements across each. Successful EMR integration initiatives can offer a substantial return on investment. Organizations often experience a 25% reduction in data entry time, a 15% decrease in errors, and an impressive 20% in cost savings. This underscores how well-executed integration boosts efficiency and financial performance.
A robust EMR integration foundation requires a thorough understanding of the underlying technical components. These components are fundamental, each playing a vital role in the system’s overall stability and functionality. Overlooking these key integration elements can compromise the entire project.
Key Technical Components for Successful EMR System Integration
Understanding the purpose, complexity, and cost implications of these components is crucial for sound decision-making. The following table provides a comparative overview of these critical technical components. It helps clarify the role and impact of each element within a successful EMR integration.
To help you understand the complexities of EMR integration, we’ve compiled a comparison of the key technical components. This table breaks down each component’s purpose, how difficult it is to implement, and the associated costs.
| Component | Purpose | Implementation Complexity | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) | Enable communication between different software systems, allowing data to flow seamlessly. They act as messengers between applications. Consider API documentation when choosing the right API for your needs. | Moderate to High | Moderate |
| Data Standards (e.g., HL7 FHIR) | Ensure data consistency and interoperability across systems. These standards act as universal translators, allowing disparate systems to understand each other. | High | High |
| Interface Engines | Manage and route data between systems, acting as a central hub. They streamline the flow of information between different parts of the EMR system. | Moderate | Moderate |
| Data Mapping | Defines how data is translated between different formats. This ensures accurate data transfer by creating a blueprint for data transformation. | Moderate to High | Moderate |
| Security Protocols (e.g., encryption, access control) | Protect sensitive patient data from unauthorized access, acting like a lock and key system. These protocols are crucial for maintaining patient privacy and complying with regulations like HIPAA. | High | High |
This table highlights the importance of considering both functionality and budget when selecting integration components. Just as with any complex project, balancing these considerations is essential for success.
Practical Considerations for Seamless Connectivity
Connecting various systems, like lab equipment and imaging devices, requires a strategic approach. For instance, integrating a lab system might involve mapping lab test codes between the EMR and the lab’s software. This ensures accurate transfer of results into patient records.
Integrating imaging devices often necessitates adhering to communication protocols like DICOM, which facilitates seamless transfer of images and reports. These examples demonstrate the need to understand the nuances of each system and plan for potential integration challenges. Addressing these challenges early in the process can greatly improve patient care and streamline workflows.
Investing in thorough planning and architectural design is essential for long-term success. A well-planned EMR integration strategy provides a stable and adaptable foundation for future growth and technological advancements. This includes considering factors like scalability, security, and future interoperability needs. This proactive approach minimizes the need for costly revisions and ensures the system can adapt to future demands. By building a strong foundation, healthcare organizations can ensure their EMR integration remains effective and relevant in the evolving healthcare landscape.
Conquering Real-World Interoperability Challenges

EMR system integration offers significant potential benefits, but it also presents a complex array of real-world challenges. These hurdles often go beyond purely technical issues and can impact even healthcare organizations with substantial resources. One frequent obstacle is vendor lock-in, where an organization becomes dependent on a single vendor, which restricts flexibility and can escalate costs. This reliance makes integrating new systems or changing vendors difficult.
Another significant roadblock is data format inconsistencies. Different EMR systems often use varying data formats, necessitating complex mapping and translation. It’s akin to trying to solve a jigsaw puzzle with pieces from different sets – they simply don’t fit together easily. For instance, one system might employ a specific code for a medical procedure, while another system uses a completely different code. This can cause confusion and potential errors when exchanging data.
This complexity adds significant time and expense to integration projects. Fortunately, solutions are being developed to address these problems.
Overcoming Vendor Lock-In and Data Silos
Smart IT teams are employing strategies to tackle these interoperability challenges. One approach involves robust negotiation tactics with vendors from the outset. Organizations can mitigate the risks of vendor lock-in by clearly outlining integration requirements in contracts and insisting on open standards. This empowers them to select the systems that best suit their needs, without being restricted by proprietary technologies.
Phased integration approaches can also minimize disruption during the implementation process. Instead of a complete system overhaul, organizations can integrate systems incrementally. This allows time for staff training and workflow adjustments, reducing the risk of overwhelming staff and ensuring a smoother transition.
Real-World Success Stories and Contingency Planning
Real-world examples offer valuable lessons in overcoming integration hurdles. One hospital system successfully integrated its EMR with a regional health information exchange (HIE), enabling seamless data sharing with other providers. This improved care coordination and reduced unnecessary testing. You can find more detailed statistics on EMR adoption and interoperability at Market.us. Despite widespread EMR adoption, interoperability remains a substantial challenge. Only about 46% of U.S. hospitals had basic EHR interoperability capabilities in 2021, despite over 90% EMR adoption. This reveals a critical gap in healthcare technology. This lack of interoperability can lead to significant costs, estimated at $30 billion in annual inefficiencies within the U.S. healthcare system.
Even the best-laid plans can encounter unforeseen issues. Therefore, it’s crucial to develop comprehensive contingency plans. These plans should pinpoint potential points of failure, outline mitigation strategies, and establish clear communication protocols. This proactive approach allows organizations to effectively address unexpected problems and maintain the integration project’s momentum. By learning from both successes and failures, healthcare organizations can effectively navigate the complexities of EMR system integration and achieve their objectives.
Mastering Cloud-Based EMR System Integration

Cloud technology is changing how healthcare organizations handle EMR system integration. This shift offers major advantages, particularly in security, scalability, and cost control. Leading health systems are recognizing these benefits and moving away from costly on-premise solutions. This allows them to redirect resources towards patient care instead of complex hardware maintenance. This transition represents a significant advancement toward more flexible and efficient healthcare IT infrastructure.
Choosing The Right Cloud Approach
There’s no single perfect solution when it comes to cloud adoption. The key is choosing a cloud strategy that aligns with your organization’s specific needs and resources. The three primary cloud models – public, private, and hybrid – offer varying levels of control, flexibility, and security. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
Public cloud offers cost-effectiveness and speed of deployment, but less control over data security. Private cloud offers greater control and enhanced security but involves higher initial investment. Hybrid cloud combines aspects of both, allowing organizations to capitalize on the strengths of each approach.
For instance, a small practice might find a public cloud solution sufficient, while a large hospital system with strict security requirements might opt for a private or hybrid cloud model. Understanding these nuances is fundamental to effective EMR system integration. A well-chosen cloud approach can support the specific operational and compliance needs of any healthcare organization.
Successful Cloud Migration Strategies
Migrating to a cloud-based EMR system requires careful planning and execution. This transition involves not only moving data, but also adapting workflows and training staff. One essential aspect is implementing strong data validation protocols. This ensures data integrity during migration, preventing data loss or corruption. It’s similar to carefully packing fragile items for a move – you want to ensure everything arrives safe and sound. Cloud-based EMR system integration is changing how patient data is managed and shared. By 2025, cloud technology became essential for EMR evolution, providing secure and scalable access to patient records. Explore this topic further.
Another vital element is developing effective staff training strategies. This empowers your team to confidently use the new cloud-based system. This includes clear instructions, hands-on practice, and ongoing support for a smooth transition. Like learning any new tool, staff needs time and guidance to master the cloud-based EMR. By focusing on data integrity and staff preparation, healthcare organizations can minimize risks and maximize the benefits of cloud migration. This careful approach ensures a seamless transition and ultimately benefits patient care.
Leveraging AI To Transform Your EMR Integration
Artificial intelligence is quickly changing how Electronic Medical Records (EMR) systems are integrated within healthcare. Organizations looking to the future are incorporating AI into their integration strategies. Their goals? Automating documentation, improving the accuracy of diagnoses, and predicting patient outcomes using integrated data. This represents a major step forward in how healthcare uses technology to improve both efficiency and the quality of patient care.
Automating Tasks and Enhancing Accuracy
AI-powered EMR integration offers real, tangible benefits. One key advantage is AI’s ability to reduce administrative work, freeing up clinicians to spend more time with patients. Imagine physicians spending less time on paperwork and more time interacting with patients. This is the potential of AI-driven automation. Intelligent alerts, powered by AI, can also enhance patient safety by proactively identifying potential risks. Unlike generic warnings, these alerts offer specific, actionable insights that can lead to better patient outcomes.
The integration of AI into EMR systems is transforming healthcare technology. By 2025, AI integration has become a core component of EMR system development. This is largely driven by the increasing demand for features like predictive analytics and automated documentation. AI can reduce administrative burdens by up to 70% in some workflows, allowing clinicians to dedicate more time to patient care. Learn more about the growing EMR market here.
The Power of NLP and Machine Learning
AI achieves these improvements through several key technologies. Natural Language Processing (NLP) helps decipher complex clinical notes. NLP extracts key information and converts it into structured data. Think of it as a digital assistant that understands and organizes the subtleties of medical terminology. Machine learning algorithms also play a crucial role, identifying patterns that might be missed by human observation. This ability to detect subtle trends can result in earlier diagnoses and more personalized treatment plans.
Practical Considerations for AI Integration
Implementing AI within EMR systems requires careful planning. High-quality data is essential for training AI algorithms effectively. Just like a student needs accurate information to learn, AI algorithms require reliable data to perform optimally. Appropriate governance frameworks are also critical to ensure the responsible and ethical use of AI. These frameworks address important issues such as data privacy, bias detection, and transparency.
AI and the Future of EMR Integration
AI is no longer a supplementary feature; it’s becoming an essential element of EMR system integration. This integration empowers healthcare organizations in multiple ways. It helps improve operational efficiency, enhance the quality of patient care, and create a more sustainable healthcare system overall. By embracing AI, healthcare providers gain the tools needed to meet the changing demands of modern medicine.
Securing Your EMR System Integration Like A Pro

Protecting patient data is paramount in healthcare. It’s not just a matter of compliance; it’s about safeguarding sensitive information and building trust with your patients. This requires moving beyond the basics and implementing robust, multi-layered security strategies within your EMR system integration. Crucially, these strategies must effectively secure your integrated systems without impacting their usability.
Essential Security Layers for EMR System Integration
Several key security measures combine to create a strong defense. Endpoint protection, much like a security guard at every door, safeguards individual devices like computers and tablets from unauthorized access and malware.
Network segmentation isolates different parts of your network. This containment strategy means that if one area is compromised, the others remain protected, much like containing a fire within a single room.
Finally, encryption scrambles data, rendering it unreadable without the correct decryption key. Think of it as storing your valuable information in a securely locked safe.
These security measures are vital, but they must also be practical in busy clinical settings. For instance, strong passwords are essential, but overly complex passwords that clinicians frequently forget can disrupt workflows and negatively impact patient care. Finding the right balance between robust security and practical usability is key.
Navigating HIPAA and Other Regulations
Successfully integrating EMR systems also requires a thorough understanding of and adherence to relevant regulations. HIPAA, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, sets stringent standards for protecting patient health information (PHI), including requirements for data security, privacy, and breach notification.
Furthermore, state privacy laws can introduce additional layers of complexity. Staying informed about these evolving regulations is essential to avoid potential legal and financial penalties.
Learning From Real-World Security Incidents
Often, the most effective way to learn about security best practices is by examining past incidents. Analyzing how breaches occurred and how they were mitigated can help identify potential vulnerabilities in your own system.
For example, a phishing attack could compromise an employee’s login credentials, potentially granting unauthorized access to the EMR system. Learning from such incidents highlights the importance of comprehensive staff training on security best practices.
Implementing robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection. This means users need a second form of identification, like a code from their phone, in addition to their password. This makes it significantly more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access sensitive patient data.
By establishing a solid security foundation and learning from past mistakes, healthcare organizations can effectively protect their EMR systems and maintain patient trust, ensuring the long-term success of their system integration.
Measuring What Matters In EMR Integration Success
True EMR system integration success isn’t just about systems staying online. It’s about seeing measurable improvements in both patient care and organizational efficiency. This requires tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) that demonstrate a real-world impact. These go beyond basic technical functionality and encompass areas like cost savings, workflow improvements, provider satisfaction, and a better patient experience.
Establishing Meaningful Metrics and Baselines
Before measuring success, you must establish a clear baseline. This means assessing your current performance in key areas like data entry time, error rates, and patient wait times. For example, if your average patient wait time is currently 30 minutes, a potential target after EMR integration might be to reduce it to 20 minutes.
Identifying the right KPIs for different stakeholders is also essential. Clinicians might prioritize patient outcome metrics, while administrators focus on cost savings and efficiency gains. This targeted approach ensures the integration’s success resonates with everyone, from frontline staff to executive leadership.
Tracking Progress and Creating Dashboards
Once baselines and targets are set, ongoing monitoring is crucial. Creating dashboards that visualize these metrics allows for easy progress tracking. These dashboards can display real-time data, highlighting improvements and identifying potential problems.
For instance, a dashboard might show a significant reduction in data entry time after integrating a new lab system with the EMR. This immediate feedback lets you quickly assess the integration’s effectiveness and make any necessary adjustments.
To help illustrate how you might track EMR integration success, let’s take a look at some key metrics. The following table outlines some examples of categories, KPIs, measurement methods, and target ranges.
EMR Integration Success Metrics
| Metric Category | Specific KPIs | Measurement Method | Target Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Efficiency | Average patient wait time | Patient tracking system | <20 minutes |
| Clinical Efficiency | Data entry time per patient | EMR system logs | <5 minutes |
| Clinical Quality | Medication error rate | Incident reports | <1% |
| Patient Satisfaction | Patient satisfaction scores | Post-discharge surveys | >4 out of 5 |
| Financial Performance | Cost per patient encounter | Financial reports | <$XXX |
This table provides a framework for thinking about which metrics are most important to track for your specific integration project. Remember to tailor these examples to your organization’s unique needs and goals.
Demonstrating the Value of Integration
Finally, effectively presenting your integration success is crucial for continued support and investment. Translating technical achievements into tangible benefits, like reduced patient wait times or improved medication adherence, helps everyone understand the value.
Think of it like building a bridge. It isn’t enough to just say it’s structurally sound. You must demonstrate how it connects communities and improves transportation. Similarly, showcasing the positive impact of your EMR integration on patient care and organizational efficiency ensures its success is recognized and appreciated by all stakeholders.
Future-Proofing Your EMR System Integration Strategy
Healthcare technology is constantly evolving. This means your EMR integration strategy needs to be adaptable without requiring costly system overhauls. Anticipating future trends and incorporating flexibility into your system’s architecture are key to long-term success. Smart healthcare leaders are already planning for the impact of technologies like blockchain and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). These innovations will fundamentally change how healthcare data is managed and shared.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact on Integration
Blockchain, known for its security and transparency, could revolutionize secure data sharing in healthcare. Imagine a future where patient records are instantly verifiable and accessible by authorized providers. This eliminates the delays and security risks inherent in traditional data exchange. This is the potential of blockchain for EMR system integration.
The IoMT is also expanding integration beyond traditional clinical systems. IoMT devices, such as wearable health trackers and remote patient monitoring equipment, generate massive amounts of data outside the hospital. Integrating this data into EMR systems creates a more holistic view of patient health, enabling more proactive and personalized care.
Building Flexibility Into Your Architecture
Successful organizations prioritize flexible architectures that can easily adapt to new technologies. This adaptability prevents the need for complete system rebuilds when a new technology emerges. Think of it as building a house with adaptable rooms that can serve multiple functions, rather than constructing a new addition every time your family grows. This adaptable approach saves significant time and resources.
One strategy for building flexibility is using modular integration components. This means designing systems with interchangeable parts that can be easily updated or replaced. This allows organizations to integrate new technologies without disrupting existing workflows. Think of it like updating your smartphone’s operating system. The core functionality stays consistent while benefiting from new features and security improvements.
Developing a Forward-Looking Implementation Roadmap
Evaluating emerging technologies requires a structured approach. A practical framework involves assessing a technology’s potential impact on your operations, evaluating its maturity and security implications, and developing a phased implementation plan. This minimizes disruptions and allows for the strategic incorporation of new tools.
For instance, integrating IoMT devices requires upfront consideration of data security and privacy, device compatibility, and clinical workflow impacts. Addressing these concerns proactively ensures smoother, more successful integration. This forward-thinking approach helps avoid costly mistakes and positions systems for future success. The goal is to create a system that not only functions effectively today but is also well-prepared for the opportunities and challenges of tomorrow.
Discover how virtual medical receptionists revolutionize healthcare communication—cutting hold times by 50% and boosting patient satisfaction with 24/7 AI-powered scheduling and intake. Ready to optimize your practice’s efficiency and patient care? Discover how Simbie AI can transform your workflows by automating administrative tasks and improving patient interactions. Learn more at Simbie AI.

